Corneal Cross Linking
Corneal Cross Linking
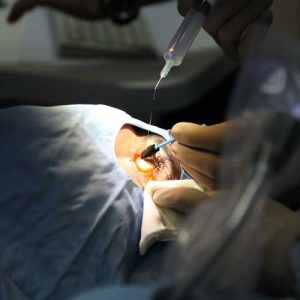 Some corneal diseases like keratoconus or the postoperative complication of LASIK surgery may result in corneal weakness and corneal ectasia. Corneal Cross Linking also known as CCL, CXL, and corneal collagen cross linking is a surgical treatment to prevent the progression of the resulting corneal ectasia.
Some corneal diseases like keratoconus or the postoperative complication of LASIK surgery may result in corneal weakness and corneal ectasia. Corneal Cross Linking also known as CCL, CXL, and corneal collagen cross linking is a surgical treatment to prevent the progression of the resulting corneal ectasia.
During the surgery, the liquid riboflavin (a vitamin of the B complex) is applied to the eye and then is activated by illumination of ultraviolet light (UVA) for about 30 minutes. It creates new collagen crosslinks between the cornea’s collagen fibers which leads to recovering and representing the cornea’s strength.
The surgery can be performed in two methods. In Epithelium-on CXL type, the epithelium layer which is the outer layer of the cornea is kept untouched so the penetration of the riboflavin into the cornea is decreased which results in using more amount of riboflavin. In the Epithelium-off CXL method, the epithelium layer is removed leading to the increment of the penetration of the riboflavin into the cornea.
After the surgery, you may face with some postoperative complications which rarely occurred including cloudy vision, haziness of the cornea, corneal epithelium defect, sensitivity to bright lights, infection, eyelid swelling, tearing, and dry eye.